Imf Forecast Nz
forecast wallpaperThe IMF forecast for Australia is for a 45 per cent contraction a significantly better outlook than New Zealands. But growing concerns about the global economy have increased the downside risks to New Zealands outlook the IMFs annual review of New Zealands economy found.
 Imf Media Center Imf World Economic Outlook January 2021 Forecast
Imf Media Center Imf World Economic Outlook January 2021 Forecast
The IMF forecasts the New Zealand economy will contract 72 per cent in 2020 in comparison with the Treasurys Budget Economic and Fiscal Update forecast of 46 per cent.
Imf forecast nz. This follows a global contraction of 35 per cent in 2020 as a result of the coronavirus pandemic. The last Article IV Executive Board Consultation was on June 25 2018. Reflecting worse-than-expected outturns in the second quarter in a few countries the IMFs forecast for the region has been downgraded to -22 percent in 2020the worst outcome for this region in living memory.
But the 19 percent full-year growth for 2020 that the IMF maintains if confirmed will be its worst showing since 1976 just before the start of its economic reform era. The IMF forecasts the New Zealand economy will contract 72 per cent in 2020 in comparison with the Treasurys Budget Economic and Fiscal Update forecast of 46 per cent. This page has economic forecasts for New Zealand including a long-term outlook for the next decades plus medium-term expectations for the next four quarters and short-term market predictions for the next release affecting the New Zealand economy.
Policy support is key to financial stability with IMFs Fabio Natalucci SDR Rates for February 11 2021 SDR Interest Rate 0090 1 USD SDR 069329 MORE The IMF and COVID-19. WASHINGTON The International Monetary Fund IMF raised its forecast for global growth this year betting that the roll-out of coronavirus vaccines and more fiscal stimulus will offset the. New Zealands economy is predicted to.
The IMF forecasts New Zealand will spend 467 of GDP this year and 445 in 2021. Hopes of a vaccine-powered rise in activity later this year have led the IMF to upgrade its forecast for global economic growth in 2021. It forecasts that between 2017 and 2021 only Hong Kong will boost government spending relative to GDP more than New Zealand.
Fresh numbers show the Labour-led administration was a big spender even before Covid-19 and New Zealand incomes overall in 2025 might be less than in 2019. New Zealands economic growth is solid and is forecast to remain close to trend the International Monetary Fund says. 44 per cent drop in global growth for 2020 13 Oct 2020 0756 PM 5 minutes to read Kristalina Georgieva managing director of the International Monetary Fund is expecting a.
Everything hinges on a successful vaccine rollout in the major economies. This follows the IMFs downgrading of the outlook for the UK economy with Britain now expected to bounce back with just 45 growth this year instead of Octobers 59 forecast. New Zealands economic expansion is still solid.
The IMF also forecasts that New Zealands real GDP per capita in 2025 will still be lower than in 2019. Their new global forecast is for growth of 55 this year and 42 in 2022. Last week the International Monetary Fund.
Forrester breaks down what the IMF report means for tech markets in 2020 and. Updated IMF forecasts indicate a deeper recession in 2020 and a shallower recovery in 2021 for the world economy. Listed below are items related to New Zealand.
The IMF has kept its growth forecast for 2022 at 42 per cent. But they also warn about exceptional uncertainty. The IMF global growth upgrade helped pro-cyclical currencies like the NZD AUD and CAD which were all up around 03 to 04 against the USD and heading the majors currency leader board.
After trading a tight 20 pip range in the local session yesterday the NZD dipped to just under 07170 late last night on the Asian equity swoon. The upgrade reflects expectations. Growth Forecast At -3 Per Cent As IMF Offers Debt Relief To Most Vulnerable Nations Wednesday 15 April 2020 846 am Press Release.
The fund IMF expects the global economy to contract by about 3 per cent in 2020 a much sharper fall than that experienced after the global financial crisis.
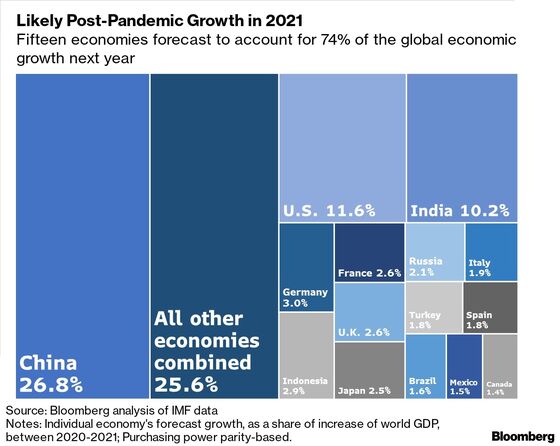
Insight/2020/08.2020/08.17.2020_EconForecasts/IMF%202020%20GDP%20Forecast%20Changes.png?width=1109&name=IMF%202020%20GDP%20Forecast%20Changes.png)

